Digital Implant Dentistry: Transforming Precision and Efficiency in Modern Implantology
Introduction
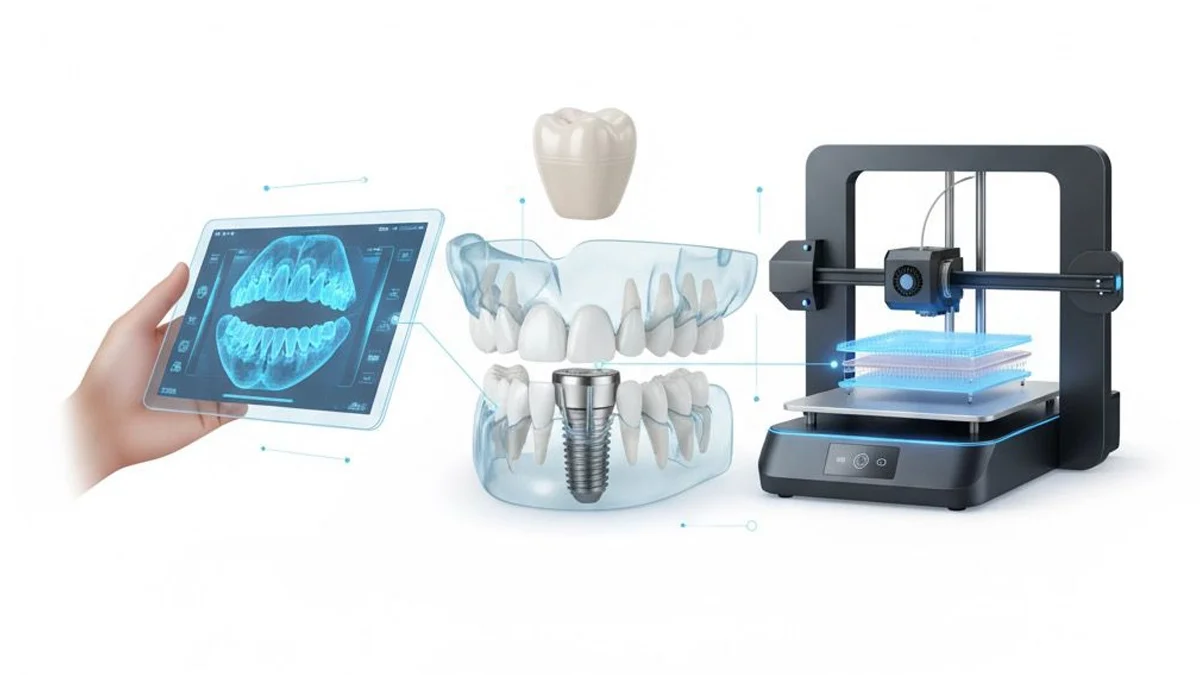
Digital implant dentistry represents a revolutionary advancement in the field of dental implantology. By integrating cutting-edge digital technologies such as 3D imaging, CAD/CAM design, and guided surgery systems, clinicians can achieve superior accuracy, predictability, and patient satisfaction. This modern approach has reshaped the traditional implant workflow—from diagnosis to final restoration.
1-What Is Digital Implant Dentistry?
Digital implant dentistry refers to the use of digital technologies at every stage of the implant process, including diagnosis, treatment planning, surgical placement, and prosthetic restoration. This fully digital workflow eliminates many of the limitations of conventional methods and provides greater control over both surgical and restorative outcomes.
Key technologies used include:
- Intraoral Scanners: Capture highly accurate digital impressions of the patient’s mouth.
- CBCT (Cone Beam Computed Tomography): Provides 3D visualization of bone structure, nerves, and sinuses.
- CAD/CAM Systems: Enable the design and milling of custom abutments and prosthetic components.
- 3D Printing: Used for creating surgical guides and provisional restorations with unmatched precision.
- Implant Planning Software: Allows virtual implant placement and simulation of the final prosthesis.
2-Advantages of the Digital Implant Workflow
The digital workflow offers numerous advantages for both clinicians and patients:
For Clinicians
- Enhanced Precision: Digital planning ensures accurate implant positioning and angulation.
- Predictable Outcomes: Virtual simulations allow for better treatment planning and risk reduction.
- Improved Communication: Seamless data transfer between clinician, lab, and patient.
- Reduced Chair Time: Faster procedures and fewer patient visits.
For Patients
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: Digital guides reduce surgical trauma.
- Shorter Treatment Time: Immediate or same-day restorations are possible.
- Comfort and Confidence: Better-fitting prosthetics and improved esthetics.
3-The Digital Implant Workflow: Step by Step
Step 1: Digital Diagnosis
The process begins with a CBCT scan and intraoral scanning, providing a detailed 3D model of the patient’s oral anatomy.
Step 2: Virtual Treatment Planning
Specialized software allows the dentist to virtually plan the implant position, depth, and angle, taking into account bone density and prosthetic requirements.
Step 3: Guided Surgery
A 3D-printed surgical guide is fabricated based on the virtual plan, ensuring accurate and safe implant placement during the actual procedure.
Step 4: Digital Prosthetic Design
Once osseointegration occurs, the final prosthetic components are designed using CAD/CAM systems for ideal occlusion, function, and esthetics.
Step 5: Final Restoration
The custom crown or bridge is fabricated and fitted with exceptional precision—often in a single appointment.
4-Tools and Systems Used in Digital Implant Dentistry
Some of the most commonly used tools and systems include:
- CBCT scanners (e.g., Planmeca, Vatech, Morita)
- Intraoral scanners (e.g., Medit, 3Shape TRIOS, iTero)
- CAD/CAM milling machines
- 3D printers (for surgical guides and provisional prosthetics)
- Digital planning software (e.g., coDiagnostiX, Blue Sky Plan, SimPlant)
5-Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits are numerous, successful digital implant dentistry requires:
- Proper training in software and digital workflow management.
- Investment in high-quality digital equipment.
- Understanding of the integration between surgical and prosthetic phases.
However, the long-term efficiency, reduced errors, and patient satisfaction make this investment worthwhile for any modern dental practice.
6-The Future of Digital Implantology
The future of implant dentistry is undeniably digital. Artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and robotics are expected to enhance digital workflows even further, enabling fully automated, precision-driven implant procedures. As technology continues to evolve, clinicians who adopt digital workflows today will remain at the forefront of innovation and clinical excellence.
Conclusion
Digital implant dentistry is transforming the way dental professionals diagnose, plan, and perform implant procedures. By combining digital accuracy with clinical expertise, dentists can achieve unparalleled results in both function and esthetics.
At West Dent, we believe in embracing innovation—supporting dental professionals with the latest digital tools, implant systems, and educational resources to deliver the best outcomes for their patients.
